Every citizen in a country has the essential right to vote. Traditionally, voting methods such as paper ballots and Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs) have been trusted and widely used. However, their centralized nature brings about ambiguity and security concerns. The reliance on a central database for storing voting data raises the risk of third-party manipulation, delays in real-time result updates, and potential impacts on system integrity and public trust in democracy and the government. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that election voting methods are legal, accurate, secure, and convenient.
Blockchain Technology in Voting Systems
To ensure the proper conduct of voting, it is essential to establish a transparent and secure process that upholds voter privacy. In this context, the challenge is to find a solution that effectively prevents unauthorized data manipulation while maintaining the desired level of transparency in security measures, thereby safeguarding both voter privacy and the integrity of collected results – a critical aspect for preserving democracy. This is where a decentralized voting system, leveraging blockchain technology, comes into play. Such a system offers inherent features of security, privacy, and integrity. Within a blockchain, every node or user operates anonymously, and each action is treated as a transaction that undergoes hashing and subsequent storage within the network.
Blockchain technology in Voting Systems
Blockchain technology has effectively addressed the limitations of current election methods, offering improved transparency, accessibility, data protection, and result verification. Despite the limited adoption of electronic voting on a national scale due to significant risks, such as potential manipulation and misuse of votes, blockchain technology presents a viable solution. The traditional voting systems rely on a central authority for vote casting and lack proper verification. A blockchain-based voting systems distribute data across multiple nodes, also eliminating the possibility of widespread hacking and data alteration. This decentralized approach ensures the integrity of votes and enables efficient verification through tallying with other nodes.
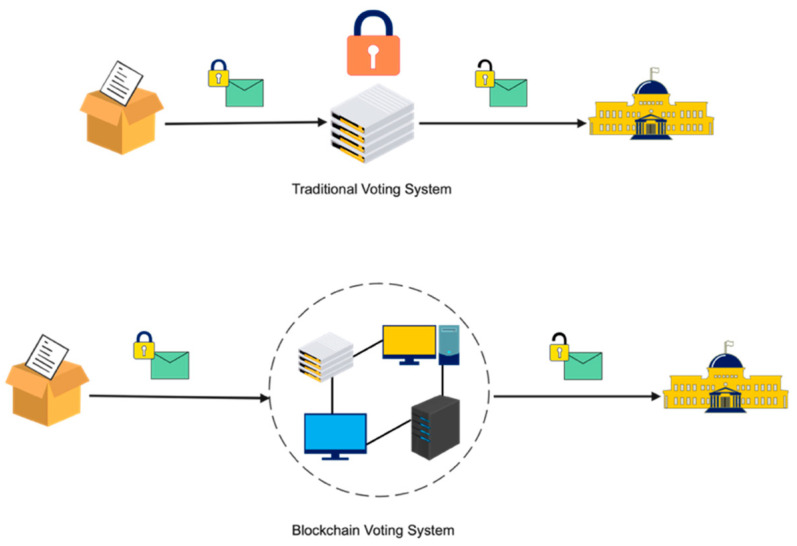
When properly implemented, blockchain technology acts as a digital, decentralized, encrypted, and transparent ledger, offering resilience against manipulation and fraud. Through the distributed structure of blockchain, a Bitcoin-based electronic voting system can effectively mitigate the risks associated with electronic elections and establish a tamper-proof mechanism. It is crucial for such a system to have a fully decentralized voting infrastructure, ensuring that no single entity, including the government, has control over the online voting process. In conclusion, the legitimacy of elections mainly relies on widespread trust in those in positions of authority. Exploring existing literature and conducting related experiments can also contribute to improving the efficiency of elections in terms of administration and participation. Furthermore, the integration of blockchain technology also introduces a novel approach to electronic voting.
Electronic Voting using Decentralized Voting Systems
Electronic voting records votes using electronic equipment, relying on hardware and software. These systems should be capable of various functions, such as setting up elections, registering voters, authenticating identities, conducting voting, and tallying results. However, the risks associated with electronic voting alone are significant, as a compromised system can have far-reaching consequences. On the other hand, blockchain technology has the potential to significantly impact electronic voting. When properly implemented, its decentralized and consensus-driven nature makes fraud theoretically impossible. Therefore, careful consideration of the unique characteristics of blockchain is also essential when designing a tamper-resistant electronic voting network. As a result, the use of blockchain technology for creating such a network is gaining traction.
In a blockchain-based voting system, each vote is encrypted and publicly stored on a distributed blockchain network. The consensus process also validates every encrypted vote, and multiple copies of the blockchain ledger store the public records. This decentralized and transparent approach allows anyone to verify the vote count while ensuring the privacy of the voters. In contrast, traditional electronic voting systems operate differently, storing votes on a single server and under the control of a central authority. Hence, the use of blockchain technology introduces a distinct organizational concept for electronic voting.
Overall, blockchain-based electronic voting enhances security and transparency while maintaining a familiar voting experience for end users.
Essential Requirements for a Trustworthy Election Process using Decentralized Voting Systems
Voting systems must meet specific security requirements to uphold the integrity and trustworthiness of elections. These requirements are essential for ensuring fair and accurate voting processes.
Accessibility and Reassurance
To ensure that every eligible voter has the opportunity to vote, the election process should provide easy access to the correct polling station. It should allow only qualified voters to cast their votes, and election officials must accurately count all ballots to ensure the integrity of the elections.
Anonymity
Throughout the entire voting process, the system must keep the correlation between registered votes and voter identities unknown, preventing external interpretation.
Verifiable Participation/Authenticity
This criterion allows for assessing whether a single voter has participated in the election. It is particularly important in cases where voting is compulsory under the constitution or in social contexts where abstention is seen as disrespectful (e.g., delegated corporate board elections in small and medium-sized organizations).
Transparency and Fairness
No one should have access to specific details before the vote count is released. This prevents manipulative actions, such as influencing late voters’ decisions through predictions or providing unfair advantages to certain individuals or groups to be the first to know the outcome.
Auditability and Accuracy
The system must ensure the accuracy of the declared results, precisely matching the actual election results. It guarantees that no one can tamper with other citizens’ votes and includes all legitimate votes in the final tally. There should be no definitive count of invalid ballots.
Robustness and Integrity
This requirement ensures that a reasonably large group of electors or representatives cannot disrupt the election process. It guarantees that registered voters can abstain or cast their legitimate votes without interference. It prohibits citizens and officials from corruptly denying election results by claiming others haven’t fulfilled their duties correctly.
Vote Privacy
After casting a vote, no one should be able to link a voter’s identity with their vote. The voting system must maintain the confidentiality of the voting relationship. This providing robust privacy as computer power and new techniques continue to evolve.
Recoverability and Identification
The voting system should track and restore voting information to prevent errors, delays, and attacks.
Lack of Evidence
While anonymous privacy safeguards against electoral fraud, it cannot guarantee protection against bribery or election rigging. This concern exists from the beginning.
Availability and Mobility
The voting systems should remain available throughout the voting period and should not restrict the location of voting.
Democracy/Singularity
A “democratic” system ensures that eligible voters can cast only one vote and prevents duplication of votes.
Voters Verifiability
Verifiability ensures that proper election auditing processes are in place. This can be achieved through uniform verification or public verification, allowing anyone, including voters, governments, and external auditors, to verify the election results after the tally has been announced. Transparent verifiability against a poll is a weaker requirement where each voter can verify if their vote has been accurately accounted for.
Genesis Convergence’s Expertise in Development and Consultancy of Decentralized Voting Systems
Genesis Convergence, a software development and consulting house, is well-positioned to contribute significantly to the development and consultancy of decentralized voting systems. Leveraging our expertise, we specialize in designing and implementing secure blockchain-based platforms, integrating smart contracts to ensure transparency and integrity throughout the voting process. Our development consulting services encompass strategic planning, risk assessment, and tailored recommendations for optimal utilization of blockchain technology.
With a focus on user-friendly interfaces and seamless integration, we actively engage in gathering initial requirements, deploying, and maintaining systems. Partnering with Genesis Convergence empowers organizations to achieve enhanced transparency, security, and efficiency in their decentralized voting systems.
