Machine Learning (ML) is a discipline that focuses on developing algorithms capable of learning from data. Over the years, machine learning has revolutionized numerous fields of research. Particularly in areas such as natural language processing (NLP) and image recognition. The appeal of machine learning lies in its ability to enhance efficiency and accuracy in tasks like predicting outcomes or interpreting data.
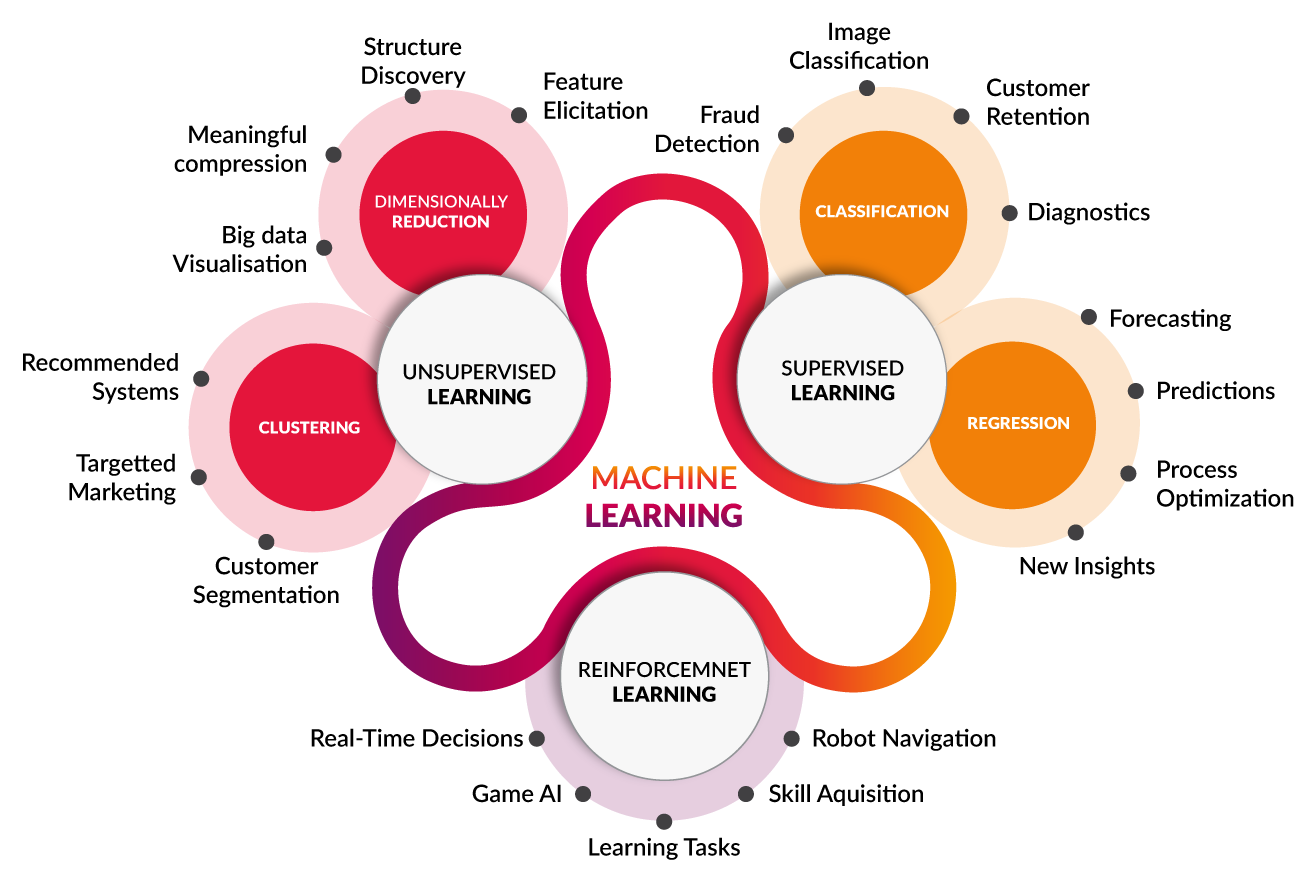
Within the realm of machine learning, various types exist, each possessing its own strengths and weaknesses. Some commonly encountered forms include:
- Supervised learning (where the algorithm is provided with labeled training data)
- Unsupervised learning (where the algorithm is presented with unlabeled data)
- Reinforcement learning (where an agent learns by associating positive negative feedback with actions)
- Deep neural networks (DNNs)
- Genetic algorithms
History of Machine Learning
The term “Machine Learning” was coined by Arthur Samuel in 1959 during his tenure at IBM. Samuel’s primary objective was to advance the field of artificial intelligence (AI), with ML as a subset of his pursuit. Following his groundbreaking discovery, there emerged a period of divergence in theories. It was not until the 1990s that AI truly gained momentum. This era became known as the “Artificial Intelligence Winter.” During this time, the focus of the field shifted from achieving general AI to solving practical problems through the application of statistical models and probability theories. Additionally, the advent of the internet played a significant role in the progress of AI, granting it access to vast amounts of data.
Use cases of Machine Learning
Currently, machine learning finds extensive application across various domains. One notable example of machine learning in action is the recommendation engine powering Facebook’s news feed. Facebook leverages ML to personalize the delivery of each member’s feed. If a member frequently engages with posts from a specific group, the recommendation engine adapts by displaying more of that group’s content earlier in the feed. Behind the scenes, the engine aims to reinforce established patterns in the member’s online behavior. If the member’s patterns change and they stop interacting with posts from that group in the following weeks, the news feed adjusts accordingly.
In addition to recommendation engines, machine learning is employed in the following areas:
Customer relationship management (CRM)
ML models in CRM software also analyze emails and prompt sales team members to prioritize the most critical messages. Advanced systems can even suggest potentially effective responses.
Business intelligence (BI)
BI and analytics vendors integrate machine learning into their software to identify significant data points, patterns, and anomalies.
Human resource information systems (HRIS)
HRIS systems also utilize machine learning models to filter through applications and identify the most suitable candidates for a job opening.
Self-driving cars
ML algorithms enable semi-autonomous vehicles to recognize partially visible objects and alert the driver.
Virtual assistants
Smart assistants combine supervised and unsupervised machine learning models to interpret natural speech and provide contextual responses. These diverse applications also demonstrate the broad utilization of machine learning techniques in various industries without triggering AI content detectors.
Future of Edge Computing
The future of machine learning holds immense significance for businesses and the practical implementation of artificial intelligence. Deep learning models, especially, are instrumental in powering advanced AI applications that have gained considerable attention. The competitive landscape of ML platforms in the enterprise technology sector is also fierce, with major vendors like Amazon, Google, Microsoft, IBM, and others vying to attract customers with comprehensive platform services. These offerings also encompass various aspects of machine learning, including data collection, data preparation, data classification, model development, training, and application deployment.
In parallel, ongoing research in deep learning and AI is increasingly directed towards the development of more generalized applications. While current AI models also require extensive training to optimize performance for specific tasks, researchers are exploring ways to enhance flexibility. They are investigating techniques that enable machines to leverage contextual knowledge gained from one task to handle future and distinct tasks.